SolarWinds warns of critical Web Help Desk RCE, auth bypass flaws

SolarWinds Web Help Desk: Five Critical Vulnerabilities, Patch Bypass History, and the Most Dangerous IT Service Management Flaw of 2026
Executive Summary
On January 27–28, 2026, SolarWinds disclosed five critical vulnerabilities in Web Help Desk (WHD), its widely deployed IT service management platform used by 300,000+ organizations globally. The batch includes:
- Two unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) flaws (CVSS 9.8)
- Two authentication bypass vulnerabilities (CVSS 9.8)
- One hardcoded credentials flaw (CVSS 7.5)
- One security control bypass (CVSS 8.8)
This latest disclosure compounds a 17-month pattern of repeated patching failures: the original AjaxProxy deserialization flaw (CVE-2024-28986, disclosed August 2024) has now been bypassed twice—in September 2025 (CVE-2025-26399) and again in January 2026 (CVE-2025-40553).
For organizations with internet-facing WHD instances, the combination of unauthenticated RCE and authentication bypass creates a critical gateway to internal IT infrastructure and sensitive data. Federal agencies face a three-week remediation deadline; commercial organizations should treat this as an emergency-priority patch.
The Vulnerabilities: A Cascade of Unauthenticated Access Vectors
SolarWinds released patches for Web Help Desk 2026.1 today, addressing six security flaws across two categories: authentication/authorization bypasses and remote code execution.
Category 1: Remote Code Execution (CVSS 9.8)
CVE-2025-40551 & CVE-2025-40553 – Untrusted Data Deserialization
Both vulnerabilities stem from unsafe Java deserialization in the AjaxProxy component, the same attack surface that has been a recurring source of failures since August 2024. The flaws allow unauthenticated attackers to craft malicious JSON-RPC requests that execute arbitrary code with NETWORK SERVICE privileges.
Attack Chain
-
Malicious JSON-RPC Payload: Attacker crafts a request targeting the AjaxProxy endpoint, including a whitelisted term (e.g.,
"java") to bypass input blacklist filters. -
Path Manipulation: Request path is changed from
/ajaxto/woto evade URI sanitization routines. -
Session Forgery: The deserialization process instantiates Java objects with properties that forge a valid user session.
-
Code Execution: The jabsorb JSON-RPC library processes the malicious object, leading to arbitrary command execution on the host.
The payloads can drop secondary malware, establish reverse shells, or exfiltrate sensitive help desk data containing passwords and service account credentials.
Category 2: Authentication Bypass (CVSS 9.8)
CVE-2025-40552 & CVE-2025-40554 – Unauthenticated Access to Protected Methods
Discovered by watchTowr researcher Piotr Bazydlo, these authentication bypass flaws allow remote, unauthenticated attackers to execute actions that should require valid credentials. Low-complexity attacks can invoke protected methods without authentication checks, granting unauthorized access to help desk functionality.
CVE-2025-40537 – Hardcoded Credentials (CVSS 7.5)
Hardcoded credentials within the WHD codebase allow attackers with low privilege to escalate to administrative functions. This pattern mirrors the critical August 2024 flaw (CVE-2024-28987), which used hardcoded username/password combinations (helpdeskIntegrationUser / dev-C4F8025E7) to grant full access to ticket data.
Category 3: Security Control Bypass (CVSS 8.8)
CVE-2025-40536 – CSRF Bypass
Cross-site request forgery protection mechanisms within WHD's WebObjects framework can be bypassed, allowing unauthenticated attackers to access restricted functionality by forging requests.
17-Month Vulnerability Timeline: A Pattern of Repeated Patching Failures
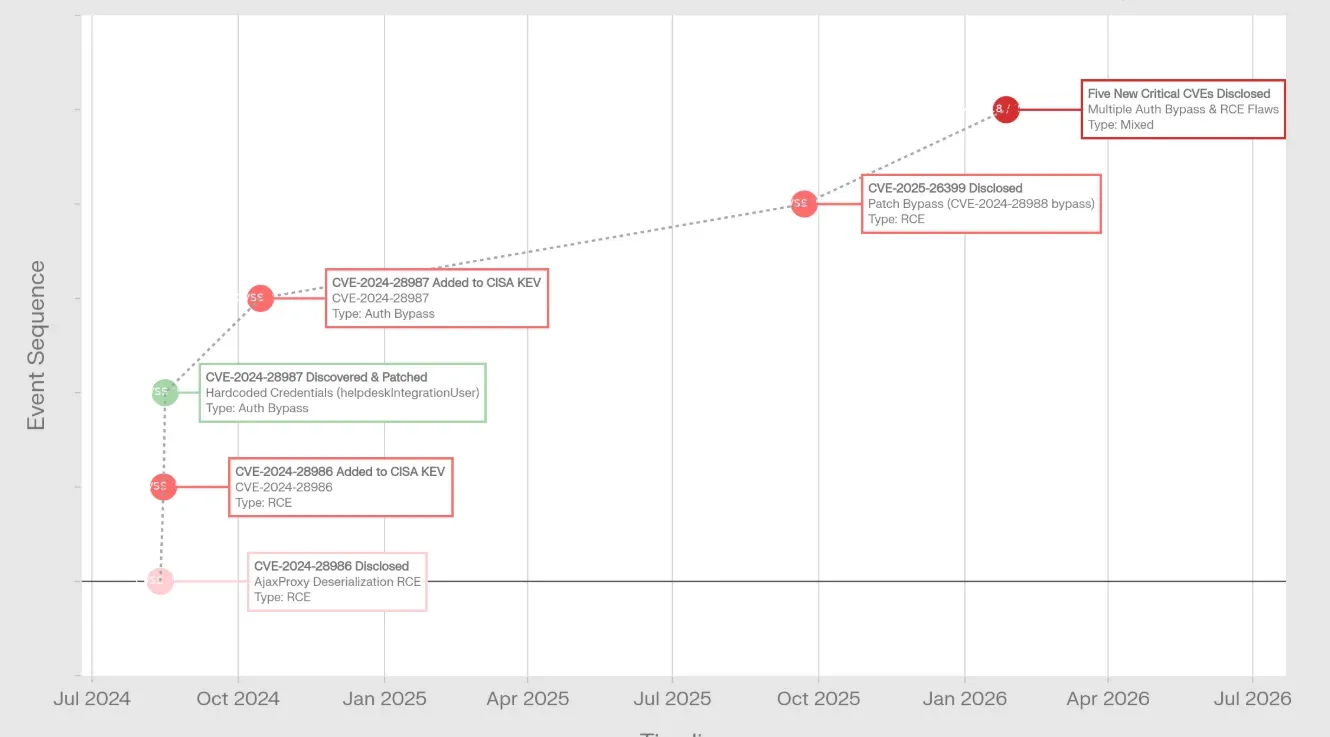
The January 2026 disclosure is not an isolated incident but the latest chapter in a cascading series of security failures in SolarWinds' flagship IT service management product.
Timeline of Failures
| Date | CVE | Severity | Event | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aug 13, 2024 | CVE-2024-28986 | CVSS 9.8 | Original AjaxProxy deserialization RCE discovered | 🔴 Exploited in wild |
| Aug 14, 2024 | — | — | SolarWinds releases first patch | ⚠️ Incomplete fix |
| Aug 15, 2024 | CVE-2024-28986 | — | CISA adds to KEV catalog | 📢 Federal mandate |
| Aug 16, 2024 | CVE-2024-28987 | CVSS 9.1 | Hardcoded credentials discovered (helpdeskIntegrationUser) | 🔴 Exploited in wild |
| Aug 21, 2024 | CVE-2024-28987 | — | Hardcoded credentials patched (5 days) | ✅ Fixed |
| Sept 22-23, 2025 | CVE-2025-26399 | CVSS 9.8 | First patch bypass of CVE-2024-28986 | 🔴 Active exploitation |
| Sept 23, 2025 | CVE-2025-26399 | — | CISA adds bypass to KEV catalog | 📢 Second mandate |
| Oct 15, 2025 | CVE-2024-28987 | — | CISA adds hardcoded credentials to KEV | 📢 Delayed addition |
| Jan 27-28, 2026 | CVE-2025-40551<br>CVE-2025-40553<br>CVE-2025-40552<br>CVE-2025-40554<br>CVE-2025-40537<br>CVE-2025-40536 | CVSS 9.8<br>CVSS 9.8<br>CVSS 9.8<br>CVSS 9.8<br>CVSS 7.5<br>CVSS 8.8 | Five critical CVEs disclosed<br>Second patch bypass<br>Authentication bypass (×2)<br>Hardcoded credentials<br>CSRF bypass | 🔴 Active exploitation confirmed |
Detailed Vulnerability History
August 2024: The Original Sin—AjaxProxy Deserialization RCE
CVE-2024-28986 (CVSS 9.8) – Java Deserialization RCE in AjaxProxy
- Discovered: August 13–14, 2024
- Reported as: Unauthenticated vulnerability (later downgraded by SolarWinds to "requires authentication after thorough testing," though advisories remained cautious)
- CISA Added to KEV Catalog: August 15, 2024
- Status: Active exploitation confirmed in the wild
- Impact: Allows arbitrary code execution on WHD servers
SolarWinds released a patch on August 14, 2024, but the fundamental deserialization mechanism in AjaxProxy was not comprehensively secured—setting the stage for two subsequent bypasses within 16 months.
August 2024: Hardcoded Credentials Surface During Investigation
CVE-2024-28987 (CVSS 9.1) – Hardcoded Credentials
- Discovered: August 16, 2024 (by Horizon3.ai researcher Jimi Sebree)
- Vulnerability Details: Credentials hardcoded in WHD codebase:
- Username:
helpdeskIntegrationUser - Password:
dev-C4F8025E7
- Username:
- Patched: August 21, 2024 (5 days from report)
- CISA Added to KEV Catalog: October 15, 2024
- Status: Active exploitation confirmed
- Impact: Unauthenticated access to all help desk tickets, including passwords, service account credentials, and sensitive personal data
September 2025: First Patch Bypass—The Second Attempt Fails
CVE-2025-26399 (CVSS 9.8) – Patch Bypass of CVE-2024-28988
Timeline Complexity: This is the third patch attempt on the same underlying AjaxProxy deserialization flaw:
- Original flaw: CVE-2024-28986 (August 2024)
- First patch bypass: CVE-2024-28988 (implied, patched before September)
- Second patch bypass: CVE-2025-26399 (September 2025)
- Disclosed: September 22–23, 2025
- Impact: AjaxProxy deserialization logic remains exploitable via alternative code paths and gadget chains
- Root Cause Analysis: Each patch iteration addressed only specific exploitable gadget chains, leaving the core deserialization mechanism fundamentally exposed
- CISA KEV Status: Added September 23, 2025
This disclosure represents a critical vendor failure: nearly one year after the original patch, attackers discovered a second way to exploit the exact same vulnerability through a different Java object instantiation path.
January 2026: Third Patch Attempt—Five New CVEs Replace Two Months of "Security"
CVE-2025-40551, 40552, 40553, 40554, 40536, 40537 (January 27–28, 2026)
- Vulnerability Scope: Authentication bypass, RCE (two variants), hardcoded credentials, security control bypass
- Active Exploitation: SolarWinds confirmed active exploitation of at least one flaw
- Patch Status: Web Help Desk 2026.1 released January 27–28, 2026
- Affected Versions: All versions through 12.8.7
- Root Cause: Fundamental architectural weakness in AjaxProxy component; insufficient input validation and access control
Comparative Analysis: SolarWinds Web Help Desk vs. The 2020 Supply Chain Attack
To contextualize the severity of this vulnerability cluster, it is instructive to compare WHD's vulnerability landscape against the 2020 SUNBURST supply chain attack that compromised 18,000 organizations, including U.S. federal agencies.
SUNBURST vs Web Help Desk Comparison
| Dimension | SUNBURST (2020) | Web Help Desk (2024–2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Compromise Method | Trojaned software updates (supply chain) | Internet-facing help desk endpoint |
| Authentication Required | Not disclosed | None (unauthenticated RCE) |
| Time to Full System Compromise | Days (multi-stage) | Immediate (single-step RCE) |
| Data Exposed | Organizational networks broadly | Help desk tickets (passwords, service accounts) |
| Patch Stability | N/A (supply chain vs. product flaw) | Failed three times in 17 months |
| Attack Complexity | High (sophisticated tradecraft) | Low (trivial JSON-RPC exploit) |
| CISA Response | Major incident; emergency directives | KEV catalog addition; 3-week deadline |
| Organizations Affected | 18,000 | 300,000+ (potential exposure) |
Key Insight
While SUNBURST required sophisticated nation-state tradecraft and supply-chain access, Web Help Desk vulnerabilities are exploitable by any attacker with network access—and many organizations have WHD facing the public internet for remote support access.
Affected Organizations and Risk Exposure
Scale of Exposure
- Total SolarWinds Customers: 300,000+ worldwide
- Estimated Internet-Facing WHD Instances: ~830 instances observed as publicly exposed (as of September 2024; current number likely higher)
- Affected Sectors: Large enterprises, healthcare providers, educational institutions, state/local government, federal agencies
Data at Risk
WHD serves as the centralized IT support ticketing platform, storing:
- ✉️ Help desk tickets with sensitive request details
- 🔑 Shared service account credentials and passwords
- 👤 Employee personal information (phone numbers, employee IDs)
- 🏗️ Internal IT infrastructure documentation
- 📋 Change request details (system access, scheduled maintenance)
Critical Risk: An attacker gaining control of WHD gains direct visibility into an organization's internal IT operations and access to credentials that unlock further lateral movement.
Active Exploitation and Threat Activity
SolarWinds has confirmed that at least one of the January 2026 vulnerabilities is actively being exploited in the wild. The combination of unauthenticated RCE + authentication bypass + hardcoded credentials creates multiple attack chains that do not require initial access:
Attack Path 1: Direct RCE
- Attacker sends CVE-2025-40551/40553 JSON-RPC payload to unauthenticated AjaxProxy
- Code executes with NETWORK SERVICE privileges
- Attacker drops reverse shell or backdoor
Attack Path 2: Credential Theft
- Attacker uses CVE-2025-40552/40554 to bypass authentication
- Attacker reads all help desk tickets (CVE-2024-28987 pattern)
- Exfiltrates hardcoded service account credentials from WHD configuration (CVE-2025-40537)
- Pivots to internal systems using stolen credentials
Attack Path 3: Chained Exploitation
- Initial foothold via CVE-2025-40551 (RCE)
- Dump database using code execution
- Extract all stored credentials and sensitive data
- Establish persistence via backdoor
Vulnerability Patch History: Why Organizations Can't Trust "Fixed" Versions
The September 2025 patch bypass (CVE-2025-26399) is particularly alarming because it reveals that SolarWinds' patch development process is fundamentally broken:
| Version | Release Date | Status | Issue |
|---|---|---|---|
| ≤12.8.2 | August 2024 | ❌ Vulnerable | CVE-2024-28986 (Original RCE flaw) |
| 12.8.3 (original) | August 2024 | ❌ Vulnerable | CVE-2024-28988 bypass (Incomplete patch) |
| 12.8.3 HF1 (hotfix 1) | August 2024 | ❌ Vulnerable | CVE-2025-26399 bypass (Second bypass) |
| 12.8.3 HF2 | September 2024 | ❌ Vulnerable | CVE-2025-26399 bypass (Third patch incomplete) |
| 12.8.7 | December 2025 | ❌ Vulnerable | CVE-2025-40551/40553 (New RCE variants) |
| 2026.1 | January 2026 | ✅ Patched | Should address all six flaws |
Critical Finding: Organizations running 12.8.7 believed they were on the latest secure version. They were not.
Remediation and Defensive Posture
🔴 Immediate Actions (This Week)
1. Apply Patches
- Upgrade to Web Help Desk 2026.1 immediately
- Verify patch deployment across all instances
- Test functionality post-patch
2. Network Isolation
- Restrict WHD access to internal networks only
- Remove from public internet if possible
- Implement VPN access requirements for remote support
3. Credential Rotation
- If WHD is internet-facing, rotate all service account credentials used by WHD
- Rotate any credentials that may have been stored in help desk tickets
- Change hardcoded default credentials immediately
4. Backup Sensitive Tickets
- Export and preserve any help desk tickets containing sensitive information before patching
- Retain for forensic analysis if compromise is suspected
🔍 Detection & Hunting
Monitor your environment for these indicators of compromise:
Suspicious Activity Indicators:
- JSON-RPC requests to /ajax/ or /wo/ endpoints
- Requests containing "java" or serialized object payloads
- Help desk database reads immediately after unknown authentication events
- NETWORK SERVICE process spawning unusual child processes
- Reverse shell connections from WHD servers
- Unauthorized access to ticket databases
- Bulk exports of help desk data
Detection Queries
Splunk Example:
index=web_logs sourcetype=solarwinds_whd
| search uri_path IN ("/ajax/*", "/wo/*")
| search request_body="*java*" OR request_body="*serialize*"
| stats count by src_ip, uri_path, method
Microsoft Sentinel Example:
CommonSecurityLog
| where DeviceVendor == "SolarWinds"
| where RequestURL contains "/ajax/" or RequestURL contains "/wo/"
| where RequestContext contains "java" or RequestContext contains "serialize"
| summarize count() by SourceIP, RequestURL, TimeGenerated
🛡️ Long-Term Controls
-
Implement Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- Block AjaxProxy access from untrusted networks
- Create rulesets for JSON-RPC payload inspection
-
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Require MFA on all WHD administrative accounts
- Implement conditional access policies
-
Database Activity Monitoring (DAM)
- Alert on bulk reads of help desk ticket tables
- Monitor for unusual database query patterns
-
Network Segmentation
- WHD should be accessible only from corporate VPN/internal networks
- Implement zero-trust architecture for IT service management tools
📊 Vendor Accountability
This 17-month pattern of patching failures—including two subsequent bypasses of the same core flaw—suggests that SolarWinds' security development practices require fundamental remediation.
Organizations should:
✅ Request a security audit of WHD's AjaxProxy and deserialization handling from SolarWinds
✅ Establish a 90-day post-patch re-assessment schedule (testing for additional bypasses)
✅ Consider alternative help desk solutions for long-term strategic planning
✅ Evaluate SolarWinds' vulnerability disclosure and patch development processes as part of vendor risk assessment
Timeline for Federal Agencies and Critical Infrastructure
Per CISA directive, federal civilian executive branch agencies have a three-week deadline to remediate critical SolarWinds Web Help Desk vulnerabilities.
| Milestone | Date | Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Disclosure | January 27–28, 2026 | CISA formal notification |
| Patch Deployment Deadline | February 17–18, 2026 | Federal agencies must patch |
| Verification | February 20, 2026 | Confirm remediation complete |
Critical infrastructure operators should adopt the same timeline as a best practice, given that help desk systems are often targeted for initial access in supply-chain intrusions.
Bottom Line
CVE-2025-40551, 40552, 40553, 40554, 40537, and 40536 represent a critical convergence of authentication bypass, unauthenticated RCE, and hardcoded credentials in a platform that manages IT infrastructure across 300,000+ organizations.
Critical Takeaways
🔴 The 17-month history of repeated patching failures—including two bypasses of the same flaw in less than one year—demonstrates that SolarWinds cannot be trusted to secure this product without fundamental architectural remediation.
🔴 Organizations must treat patching as emergency-priority, remove WHD from the public internet immediately, and rotate all service account credentials that may have been exposed.
🔴 For federal agencies and critical infrastructure operators, the three-week remediation deadline is a regulatory requirement; for commercial organizations, it should be treated as an operational emergency.
Why This Is Worse Than SUNBURST
This vulnerability cluster is worse than the original SUNBURST supply chain attack in one critical dimension:
It requires zero initial access and affects even organizations running the latest versions.
References
-
CVE-2025-40551 & CVE-2025-40553 AjaxProxy Deserialization RCE
-
Bleeping Computer - SolarWinds Warns of Critical Web Help Desk RCE and Auth Bypass Flaws
-
SecurityOnline - SolarWinds Web Help Desk Hit with Multiple RCE and Auth Bypass Vulnerabilities
-
CyberKendra - Critical Unauthenticated RCE Flaw Exposes SolarWinds Web Help Desk
-
CtrAltNod - SolarWinds Fixes Critical Web Help Desk RCE Flaws Under Attack
-
HelpNetSecurity - SolarWinds fixes critical Web Help Desk RCE vulnerability (CVE-2025-26399)
-
TheHackerNews - SolarWinds Releases Hotfix for Critical CVE-2025-26399 Remote Code Execution
-
RunZero - Latest SolarWinds Vulnerabilities: How to Find Affected Assets
-
ZeroPath - SolarWinds Web Help Desk CVE-2025-26399: AjaxProxy Deserialization RCE Summary
-
CERT-EU - Critical Vulnerability in SolarWinds Web Help Desk (September 2025)
-
CVE Details - CVE-2024-28986: SolarWinds Web Help Desk Java Deserialization RCE
-
SentinelOne Vulnerability Database - CVE-2024-28986: SolarWinds Web Help Desk RCE
-
Arctic Wolf - CVE-2024-28986 & CVE-2024-28987 Follow-Up: New SolarWinds Hotfix
-
Security Affairs - CISA Adds SolarWinds Web Help Desk Bug to Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog
-
SecurityWeek - CISA Flags Critical SolarWinds Web Help Desk Bug for In-the-Wild Exploitation
-
CyberSecurityDive - CISA Adds SolarWinds Flaw to Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog
-
Horizon3.ai - CVE-2024-28987: SolarWinds Web Help Desk Hardcoded Credential Vulnerability Deep Dive
-
CIS Security - Guiding SLTTs Through the SolarWinds Supply Chain Attack
-
TechTarget - SolarWinds Hack Explained: Everything You Need to Know
-
SolarWinds Documentation - Web Help Desk 2026.1 Release Notes
-
CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog - SolarWinds (August 2024)
-
CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog - SolarWinds (October 2024)
-
SOCDefenders.ai - SolarWinds Web Help Desk Critical Vulnerabilities Summary